

Injection molding is a highly popular technique used for manufacturing plastic parts, primarily because of its capacity to produce large quantities of identical parts. The process of injection molding is fairly straightforward, involving just two primary steps: acquiring the mold, and utilizing it to fabricate parts. Additionally, in most situations, injection molding is the most economical method for producing parts in moderate to high quantities.
Table of Contents:
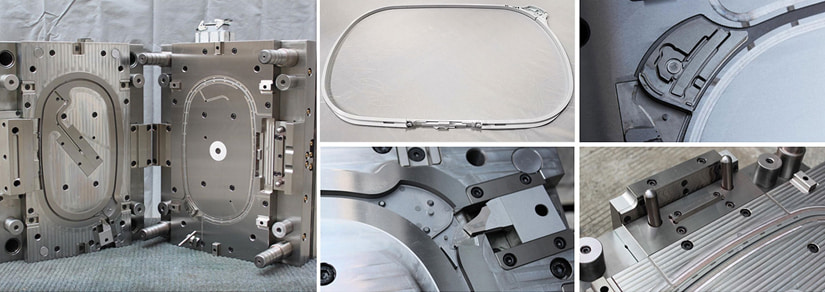
Injection molding is a manufacturing process used to produce parts or products in large quantities. It involves injecting molten material, typically plastic, into a mold cavity under high pressure. The molten material is forced into the mold, which is usually made of steel, and then cooled to form a solid part or product.
The injection molding process begins with the material being melted in a heated barrel, where it is mixed and then injected into the mold cavity using a plunger or screw. The material is then cooled and solidified in the mold before it is ejected.
Injection molding is widely used in various industries, such as automotive, medical, and consumer products, due to its ability to produce complex shapes with high precision and consistency. It is also a highly efficient and cost-effective method of manufacturing large quantities of parts or products.
Plastic injection molding is a specific type of injection molding process that is used to produce plastic parts or products. In this process, plastic material is melted and then injected into a mold cavity under high pressure, where it cools and solidifies to form the final product.
The plastic injection molding process starts with plastic pellets or resin being fed into a heated barrel of an injection molding machine. The plastic is then melted and mixed, and under high pressure, it is injected into a mold cavity that is typically made of steel. The plastic then cools and solidifies in the mold, taking on the shape of the cavity.
Once the plastic has solidified, the mold is opened, and the part is ejected. This process can be repeated many times to produce large quantities of identical parts.
Plastic injection molding is used to produce a wide range of plastic products, from small precision parts to large automotive components. It is a highly versatile and efficient manufacturing process that allows for high precision and consistency, making it a popular choice for many industries.

Injection molding is a manufacturing process used to produce parts or products in large quantities. Here is an overview of the injection molding process:
Material Preparation: The first step is to prepare the material, typically plastic pellets, which are fed into the hopper of the injection molding machine.
Melting: The plastic pellets are melted by the heating element inside the injection molding machine.
Injection: The molten plastic is then injected into a mold cavity through a nozzle and runner system.
Cooling: The plastic inside the mold cavity is then cooled and solidified by a cooling system.
Ejection: Once the plastic has cooled and solidified, the mold is opened and the part is ejected from the mold.
Post-processing: The finished part may require additional post-processing, such as trimming, drilling, or painting.
Injection molding is a highly automated process that can produce high-quality parts with tight tolerances and intricate shapes. It is used in a variety of industries, such as automotive, medical, consumer goods, and electronics.
Thermoplastics are commonly used for injection molding by plastic part manufacturers. These polymers become molten at high temperatures and solidify at cooler temperatures. Unlike thermoset plastics, they can be heated and cooled multiple times before degrading. Thermoplastics are usually in pellet form and can be mixed with additives such as colorants, recycled materials, or glitter.
The most popular thermoplastics for injection molding is Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which is a rigid and lightweight material commonly used in manufacturing LEGO bricks. Polycarbonates are transparent, impact-resistant, and used in eyewear lenses, medical devices, and bullet-proof glass. Nylon has unique electrical properties and toughness and is used in sports equipment and industrial components. Polypropylene, which is flexible, has good chemical resistance and is ideal for food containers or utensils. Finally, Polyethylene is versatile and commonly used for plastic containers and bags due to its high ductility, tensile strength, impact resistance, low moisture absorption, and recyclability.
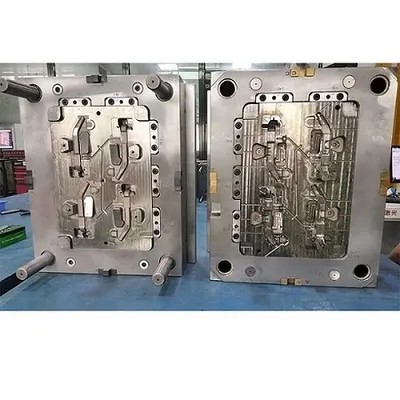
A plastic injection molding machine consists of several major components, including the injection unit, the clamping unit, and the control system. Here is a general overview of how the plastic injection molding machine works:
Injection Unit: The injection unit is responsible for melting and injecting the plastic material into the mold cavity. The process starts with the plastic pellets being fed into the heated barrel of the injection unit. The plastic is then melted and mixed before it is injected into the mold cavity using a plunger or screw.
Clamping Unit: The clamping unit holds the mold together during the injection process. It consists of a stationary platen and a moving platen that are held together by hydraulic cylinders. Once the mold is clamped shut, the plastic is injected into the cavity at high pressure.
Cooling: Once the plastic material has been injected into the mold cavity, it is cooled and solidified using water or other cooling methods.
Ejection: After the plastic has cooled and solidified in the mold, the clamping unit opens, and the part is ejected from the mold.
Control System: The control system monitors and controls the various parameters of the injection molding process, including temperature, pressure, and timing.
The entire process is highly automated and controlled by the machine's computer, which ensures precision and consistency in the final product. The plastic injection molding machine can be used to produce a wide range of plastic parts and products with high efficiency and consistency.






 Call us on:
Call us on:  Email Us:
Email Us:  No.23, XingYi Road, Wusha Community, Chang'an Town, Dongguan City, Guangdong Province, China.
No.23, XingYi Road, Wusha Community, Chang'an Town, Dongguan City, Guangdong Province, China.